Table Of Content
Bacteria can then take over and cause an infection known as folliculitis, which leads to the development of a cyst. Certain diseases or trauma to your skin can also cause them. Every pore on your skin contains a hair follicle, some fine and some coarse. Pores are the small holes in our skin that allow sweat and oil to reach the surface of the glands underneath.
More on Skin Problems and Treatments
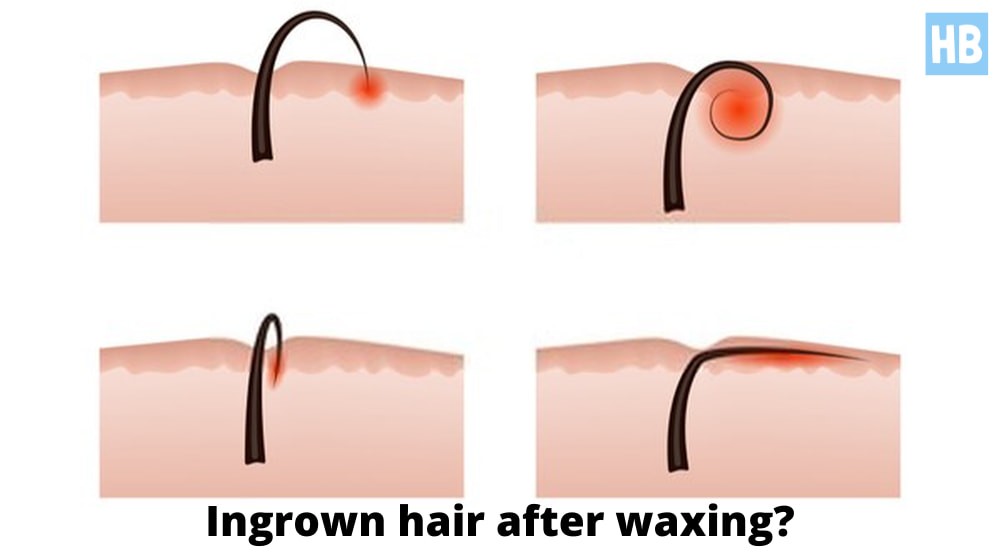
And the hair types mentioned are much easier to curl back into your skin rather than grow outwards. An ingrown hair occurs when a hair grows back into the skin rather than growing out of the skin. Ingrown hairs are also more common in areas where the hairs have been removed by shaving, tweezing, or waxing.
Cysts
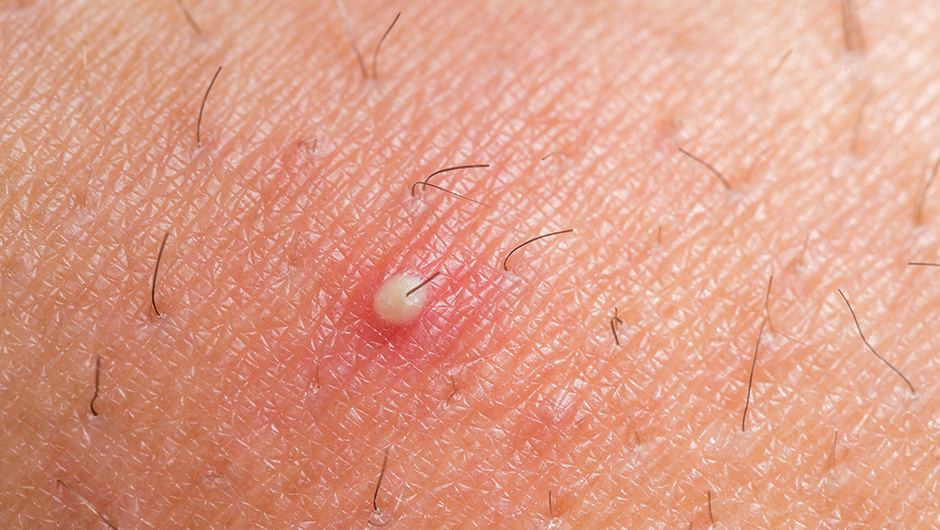
Most mildly infected ingrown hairs heal on their own but it’s important to ensure you don’t miss any signs of a severe infection. This can lead to inflammation, redness, irritation, and the formation of tiny, irritated, and painful bumps. Ingrown hairs commonly occur in areas where hair is frequently removed, such as the face, neck, armpits, legs, and groin area. Infections can develop around the ingrown hair, causing pus formation, discoloration and pain, though.
Get the Mayo Clinic app
Ingrown hairs are also known as razor bumps, shave bumps, ingrown hair bumps, or barber bumps. Hair structure and direction of growth play a role in ingrown hair. Shaving creates a sharp edge on hair, making it easier to pierce the skin.
Popular products from this list
Regular ingrown hairs or mildly infected ingrown hairs can be left alone until the condition resolves. It also helps if you don't shave the area or try alternative hair removal methods and techniques. However, your doctor may prescribe antibiotic medication or creams if you develop more severe ingrown hair issues such as cysts or folliculitis. An ingrown hair occurs when a hair that you've shaved, waxed, or plucked grows back into your skin. This can cause red, swollen, and infected hair follicles.
Preventing ingrown hair cysts
This may be due to preference, cultural values, or work requirements. Whatever the reason may be for wanting or needing to shave, there are other ways to prevent ingrown hairs. If they’re not infected, some ingrown hair cysts can go away on their own. In some cases, there’s another underlying cause, such as a genetic mutation, which means they can develop again. The only way you can prevent ingrown hairs from occurring at all is to refrain from hair removal altogether. Mild infections are less noticeable and usually clear up without treatment.
How to Treat an Ingrown Hair Cyst
If you allow your hair to grow out fully, there won’t be an opportunity for the hair to become ingrown. People who are in the military or a police force also frequently develop ingrown hairs since they are often required to shave their facial hair frequently. Folliculitis is often caused when hair follicles are infected with bacteria, commonly Staphylococcus aureus (staph). It may also be caused by viruses, fungi, parasites, medications or physical injury. Whether you shave, wax, or tweeze, removing hair isn’t always trouble-free. The process can cause swelling, irritating your skin, and leading to razor bumps and cysts.
It will not have a visible head and may be red, white, or yellow. Preventing ingrown hairs is the best way to keep cysts from developing around them. However, this type of cyst is usually harmless and will often go away without treatment.
The Pro's Guide to a Smooth Shave and Treating Razor Bumps - Vogue
The Pro's Guide to a Smooth Shave and Treating Razor Bumps.
Posted: Fri, 06 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Shaving against the grain can increase your chance of developing an ingrown hair since this can cause the sharp tip of the hair to retract into the skin. The most common complication is lasting hyperpigmentation after the inflammation has gone down. Hyperpigmentation can last for several months or longer after the ingrown hair has improved. If you notice some darker patches of skin, you can apply a topical retinoid which may improve the hyperpigmentation. Use of this website and any information contained herein is governed by the Healthgrades User Agreement. The content on Healthgrades does not provide medical advice.
If you see signs of infection, you should visit your healthcare provider. It is also possible to develop a bacterial infection, especially if you are scratching at the ingrown hair. If you notice signs of infection—like pus, worsening pain, or lesions—see a healthcare provider so they can offer proper treatment.
Treatment for ingrown hair cysts varies depending on the type of cyst involved. Some cysts may need to be treated with antibiotic ointment or surgery, while others may not need any treatment at all. If ingrown hairs won’t take a hike, you may need to forgo shaving, waxing or tweezing that area. Consider alternative hair removal options, like laser hair removal. This method targets the hair follicle, and it’s usually permanent. And because the hair doesn’t grow back after treatment, you won’t have to worry about ingrown hairs.
If you have a more serious infection that doesn't clear up quickly or worsens, you should contact your doctor. The condition is also called pseudofolliculitis barbae. It develops when shaved hairs curve back into the skin, leading to inflammation. Infected ingrown hairs can vary in severity and appearance. They can lead to increased inflammation, pain, and the formation of pustules or cysts. If an infection develops and worsens, you may need medical treatment.
These infections respond well to antibiotics, which a person may take orally or apply topically. In rare cases, an individual may need intravenous antibiotic treatment if the infection has spread throughout their body. Staphylococcus is the name for a group of over 30 different types of bacteria. One type of staph that lives naturally on human skin is Staphylococcus aureus. About 30% of people also have this bacterium living in their nose, although it may not cause symptoms.
Retinoid creams are effective in removing dead skin cells that may contribute to ingrown hairs. They can also help reduce scars from former infections. Many types of bacteria can cause infections in an ingrown follicle. While not all ingrown hairs will contract an infection with staph, some can develop this type of infection from a bacterium that usually lives on the skin.
Usually, cysts do not hurt unless an infection develops. An infected cyst may make the skin red or discolored, itchy, and tender. Don’t try to lift the hair out with tweezers like you might with typical ingrown hair. At this point, your hair is embedded far too deep underneath the bump or cyst for you to pull it out. When it comes to razor bumps, the cause is usually improper hair removal techniques. The hair grows from the bottom of your pore and is kept bathed in sebum secreted by the pore.